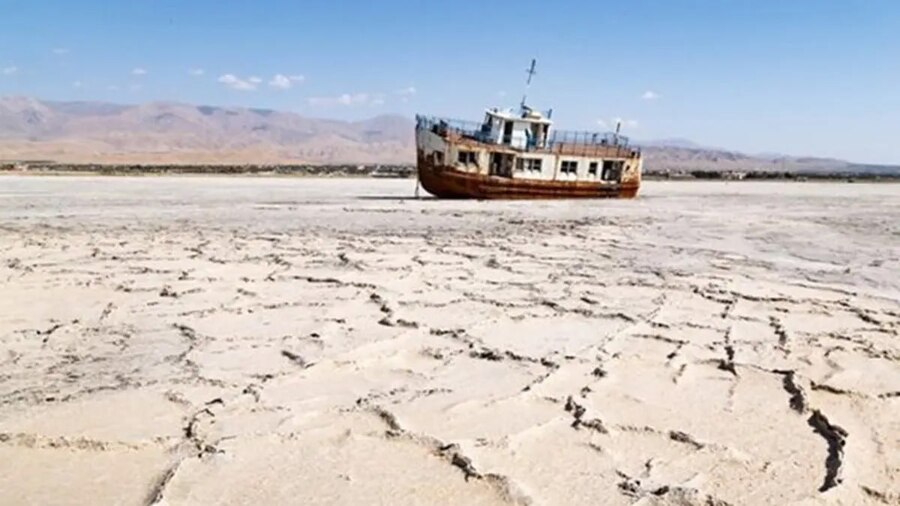
Urmia Lake
Urmia Lake is located in northwestern Iran, between East Azerbaijan province and Urmia province in the East part of Kurdistan. This lake has been full of water throughout history and until a few years ago welcomed visitors and tourists and is known as a symbol of the region.
Urmia Lake, the second largest saltwater lake in the world, is also the largest inland lake in Iran. Before drying up, it was the largest permanent lake in Great Kurdistan and the largest lake in the Middle East. Unfortunately, this lake has been drying up for several years and has become a desert and has become a major environmental threat that endangers the lives of humans and animals in the area.
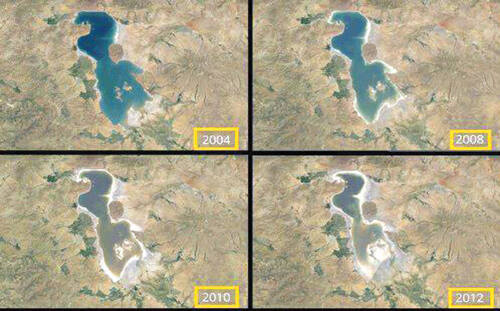
But what caused Urmia Lake to dry up?
Between the 2000s, the lake dried up and is still in danger of extinction. Since 2015, according to satellite research, it had lost 88 percent of its area and very little water was visible only in the north of the lake.

Environmental experts attribute the drying up of Urmia Lake to the following:
1. Drought causes, which according to research caused only 5 percent of drought.
2. Human factors, which include the following:
* Excessive construction of more than 70 large and small dams on the main sources of the waters that flow into Urmia Lake, in order to develop the agricultural sector and urban drinking water, and the excuse of not mixing sweet and salt water.
* Construction of a 15-kilometer highway between Urmia and Tabriz and leaving only one kilometer for water traffic between the two parts.
* Excessive use of groundwater and drilling of deep wells along the coastline of Urmia Lake from north to south in order to develop agriculture and eventually dry up all groundwater resources or decrease them significantly.
As we have already mentioned, only 5 percent of the cause of the drying up of Urmia Lake is due to nature and drought, the rest is due to wrong policies, lack of environmental management, and inappropriate policies of states during the lifetime of the Islamic Republic.

The drying up of Urmia Lake creates many dangers and crises for people and the geography of the region, which can be mentioned as follows:
1. Climate change from moderate to tropical and the emergence of winds and storms that cause changes in the environmental demography of the region with an area of more than 500 kilometers.
2. Increased diseases, especially cancer, skin, and lung diseases, due to polluted and toxic air.
3. Evacuation of cities and villages and forced migration of more than 13 million people due to salt and acid rain.
Urmia Lake, which for years welcomed many tourists for tourism and medical treatment, has now become a major threat to human life due to negligence and lack of appropriate environmental policies. In case of its extinction, many people will die or be forced to migrate. And eventually, cause political and social problems.
Although in the past four or five years, under pressure from environmental organizations inside and outside Iran and the exacerbation of the environmental crisis globally, the Islamic Republic has taken some steps to reduce the damage and prevent the complete drying up of Urmia Lake. However, only further depletion of Urmia Lake has been prevented and the main crisis remains.

When it comes to the lack of environmental policy, lack of management, and lack of science, it is that the managers of the Islamic Republic are trying to solve the drying up of Urmia Lake by creating another issue in another region!
In recent years, the government has drafted several plans to transfer water to Urmia Lake, most of which have not reached the implementation stage and have been canceled. The only project they worked on was the water transfer of the Little Zab River, located in the East part of Kurdistan in the cities of Piranshahr and Sardasht.
The government is trying to transfer water to Urmia Lake by building four or five large and small dams on the Zab River and its main source, and more than 40 kilometers of underground tunnels.
However, environmentalists and residents of Sardasht and Piranshahr have opposed these projects and have conveyed their protests to the government agencies, but unfortunately, they have not received any response.

Transporting water at a rate of 870 million cubic meters per year can have several negative impacts on the environment in the region. Also, building this number of dams in a geography with an area of only 250 square kilometers can create many other environmental problems and damage that we can mention the following possibilities:
1. Decrease in groundwater in the area behind the dams.
2- Effect on the Piranshahr earthquake zone and the possibility of reactivation of this zone and the occurrence of disasters.
3. Climate change in the region due to the presence of a significant number of dams in a geography with a small area and from cold, mountainous, and moderate climate to very hot climate.
4- Possibility of landslides due to groundwater pressure, especially in the Lajan plain in Piranshahr.









