Kurdistan Location
“Kurdistan” means a center where Kurds are in the majority and outnumber all other minorities.
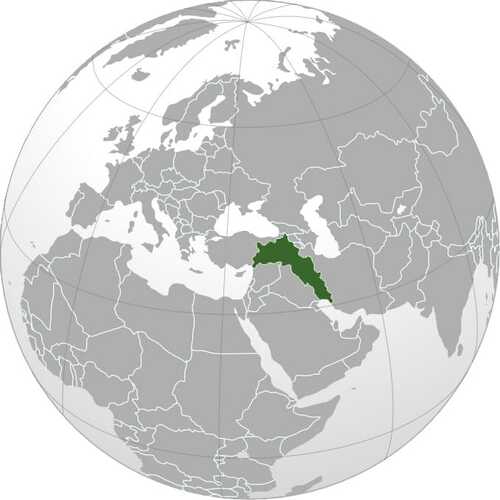
In terms of geographical location, Kurdistan is located between 34 degrees to 40 degrees north latitude and 38 degrees to 48 degrees east longitude. The center is located in the central part of the square, which is north and southwest of the Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, north and southwest of the Caspian Sea and the Gulf are the four corners.
Kurdistan is about 1000 kilometers long from west to east and 300-500 kilometers wide. Considering the geographical location of Kurdistan, this center is located between the tropical and desert climate and the Mediterranean climate (Mediterranean Sea).
Kurdistan is located in Southwest Asia. It is bordered by Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Turkey to the north, Iraq to the south, Iran to the east, and Syria to the west. Kurdistan is about 1300 kilometers long from north to south and about 550 kilometers wide from east to west. Dr. Abdul Rahman Qasemlu estimated the area of this region at 409650 square kilometers, while Western researcher Graham estimated it at 500000 square kilometers.
The geographical location, the special topographical situation, and the passage of the rainmaker air have created a favorable climate and regional diversity in Kurdistan. Meanwhile, favorable rains and snowfall in the mountainous areas have created the largest "drainage field" in the Middle East.
Kurdistan's position in the field of energy resources
Currently, jobs, agriculture, services, food production, import and export, military, medical and pharmaceutical activities, scientific research, etc. depend on energy. In this regard, the sources of energy supply, the ways of sending energy, the market for energy consumption, trade, etc. are of great importance.
The events of the first decade of the 21st century in the development of energy-related issues suggest that in this area and at the international level, the energy geopolitical game has a strategic process.
Energy geopolitics focuses on studying the role and influence of energy and its various dimensions on the policies, forces, and occasions of nations and states.
Kurdistan has a good position in the field of energy geopolitics in the region and even in the world. Kurdistan's most important energy source is crude oil reserves. Kirkuk is located in southern Kurdistan, at the foot of the southern part of the Zagros Mountains, one of the world's largest oil fields.
The oil fields of northern Mosul and Khanaqin, the Kermanshan and Ilam fields in East Kurdistan, the Garzan, Gurmak, and Ramanda oil fields in North Kurdistan, and the oil fields of northeastern Syria are among the resources that are of great economic and political importance to this region has given the Middle East. The importance of Kurdistan's oil resources is not only due to the abundance of its fields but also the very low cost of the oil wells in Kirkuk.

Kurdistan's position in the field of water resources
Given the trend of population growth and development, the future world will face problems in access to natural resources, one of which is water the countries and nations will face.
Kurdistan's geographical location, high mountains (Ararat, Zagros, etc.), proximity to the Mediterranean Sea, and the Atlantic Ocean, and the effect of receiving humid western air have provided favorable conditions for rainfall in Kurdistan.
Kurdistan is the source of many rivers and freshwater sources in the Middle East. The famous rivers of Tigris and Euphrates, Aras, Large River and Small River, Sirwan, Sefid rud, Tatahoo, Jaghatu, Gadar, Karasu, and part of Karkha originate from Kurdistan. Kurdistan's water sources flow into the Caspian Sea, the Gulf, Lake Urmia, and the Black Sea and Turkey, Iran, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Syria, and Iraq depend on Kurdistan's water.
Therefore, Kurdistan has one of the richest water resources in the Middle East and will be of great importance in terms of water geopolitics in the future.










