The basic geopolitics foundations of every State are on some points including:
1. Place
2. The area and the type of State
3. Topography
4. Weather conditions
5. Demography
6. The raw materials and industry capabilities
Each one of these points is considered to be a building block for the State’s and nations’ welfare. Let us take a look at these points about Kurdistan.
1. Place
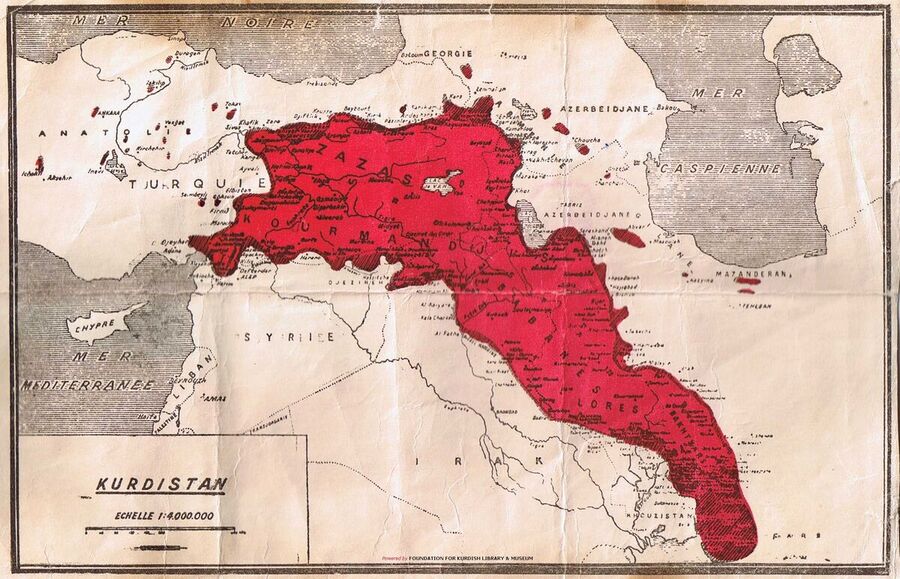
Vladimir Minorsky, the Russian orientalist and expert in Kurdish subjects, comments on determining the natural borders of Kurdistan as the following: In order to determine Kurdistan borders we need to consider two important points. The first one is the Ararat Mountains and the second one is the Eskandarouniyeh Bay. From the south of Ararat mountains, a large chain of mountains as long as one thousand kilometers stretches throughout the south; then it divides into some branches and changes its direction towards the southeast until it reaches the bay.
That map was published in Amin Zakibag’s book, “Kurd and Kurdistan”, and he wrote about it as follows: Based on the map of Kurds’ tribes (Sir Mark Sykes), the ethnographic map (Four centuries in Iraq by Major Longrigg), the map made by the Nation Society and a secret map made for the Indian Official in 1912 (2612 Kurdish year) which were mostly made by the dominant countries over Kurdistan land, cannot deny this fact that Kurdistan ends up on two bays, one from the south and the other one from the west that reaches the Mediterranean Sea.
According to what Minorsky claims, Kurdistan is between the longitude of 36 to 48 from the east and the latitude of 29 to 40 from the north. Regarding this location, most parts of Kurdistan would have moderate weather due to its closeness to the Mediterranean Sea and this location makes Kurdistan a place with large amounts of rainfall with fertile fields for agriculture that results in food abundance in the area.
Kurdistan is among for domineering countries however, as Winston Churchill once said; we don’t have everlasting friends but we have everlasting benefits. Those who are our friends today may not remain a friend in the future and vice versa.
2. The area and the type of State
The second building block to maintain a State is the area on which that state is ruling. The type of the State affects the foreign policies of a country towards its neighboring countries and other countries in the world. The best kind of land for a country is a united land that is not easily torn apart. Kurdistan is an amalgamated land but it is in form of a triangle. It is stretched down from the south away from the central parts of Kurdistan which are located in the north part. This can be a weak point during military wars.
The Capital city of every country must be at the center of that country away from the borders so that all the military and non-military activities that are carried on in a country along with the orders that must be announced by the Capital city to the other parts of that country would be carried out the best way possible. From the time of Mir ruling over Kurdistan to the contemporary era, several Capital cities have been determined so far which include Suleimani by Sheikh Mahmud, Mahabad during the Kurdistan Republic, Hewler (Erbil) from 1992 (2692) up to now.
Kurdistan’s land is about 500,000 square kilometers thus it can be considered as a medium-sized country.
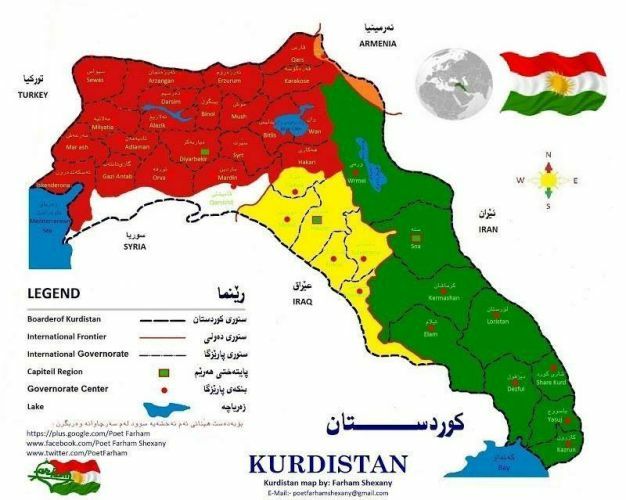
3. Topography
Undoubtedly height plays an important role in a State’s significance. The best geography is the plains because they are perfect for agriculture and residence of the citizens in cities, and building roads and railroads. The worst kind is the deserts since they are not a place for living, agriculture, or building roads. Fortunately, there is no desert in Kurdistan. Generally, Kurdistan has a mountainous topography. The highest mountain in Kurdistan is Ararat with a height of 5000 meters from sea level. These mountains have been the only support for Kurds to survive enemies’ invasions. Kurdistan is also rich in rivers and drinkable water sources. Some of the most important rivers in Kurdistan include Tigris, Euphrates, Sirvan, Zei Gawra (the great Zei), Zei Bichouk (the small Zei), Aras and … there are also some valuable plains for agriculture such as Sharazour, Kermashan, Bitwen, Jazira, … in which wheat, barley, and pea are harvested. These products are considered to be strategic products for the welfare of a country.
4. Weather conditions
As the topography of mountainous areas, as well as the fertile plains of Kurdistan, are important and affect the economy and strategies of a State; the weather conditions also play a significant role. The harshest weather is either too cold or too hot. This condition does not let the citizens be able to harvest any product or even live in suitable conditions. Fortunately, there is no such place in Kurdistan. The Northern parts of Kurdistan have cold and damp weather with forests and agricultural opportunities particular to cold weather conditions. As we move towards the south of Kurdistan the weather gets warmer and agricultural products change based on the weather conditions. These characteristics enable Kurdistan to have every kind of agricultural product during the year.
The area of Kurdistan is rather narrower that the neighboring countries which have helped people of various regions of Kurdistan to be able to move to summer houses and move back, too.
5. Demography
The name Kurdistan, meaning the country of the Kurds, is suitable to describe it since the majority of the citizens are Kurds. However, there are other ethnicities living in this area like Assyrians, Armenians, Arabs, Turkmans, and …
The mountainous nature and as a result separation that has happened for different regions of Kurdistan, the neighboring states that have dominated a part of Kurdistan under their rule have led to Kurdish people staying apart from each other. People in the South and East parts of Kurdistan write in the Aramaic alphabet, the North part of Kurdistan writes in the Latin alphabet, and those Kurds who inhabited in the Soviet Union before used to write in the Slavic alphabet. Each of these can be a weakening point in the Colonialist situation of Kurdistan.
The Kurdish language has several dialects such as Northern Kurdish, Central Kurdish, and Southern Kurdish. Each one of these dialects includes several subdialects and accents.
Just like the variety in dialects in Kurdistan, a variety of religions have also existed and been accepted in Kurdistan historically. Most of the Kurdish people are Muslims in both Shia and Sunni branches. The Shia Kurds live in the Kermashan (Kermanshah), Ilam, Lorestan, Khanaqin, and Mandali regions. The Dersim region in the North part of Kurdistan belongs to Alavi religious clans. A part of Kermashan and Lorestan belong to the Yarsani religion. The Yezidi Kurds live in Mosul and Shangal.
There has never been an accurate census in Kurdistan so far and the dominant States have always attempted to claim that the population of Kurdistan is less than the true number. However, the researchers have estimated that the Kurdistan population is about 4000000 people which seems to be logical based on the area in which these people are inhabiting in.
6. The raw materials and industry capabilities
Since Kurdistan has been divided into four parts among four states, the economic condition of the regions and areas of Kurdistan is feebler than the other countries. In comparison with the developed regions of these countries, the agriculture of Kurdistan is still managed traditionally without being modernized. The industry capabilities are also very primary. The dominant countries that rule different parts of Kurdistan have established their industrial companies and factories in their Capital cities or central regions while they extract the raw materials from Kurdistan and they take Kurdish people to those companies and factories to work for them. Despite this fact, Kurdistan is still a rich area among the countries of the world for possessing oil.
Kurdistan oil and gas wells are located in Kirkuk, Mosul, Kermashan, Sirt, and Jazira.
Kurdistan is among the richest countries for its mineral sources. Gold, iron, and other elements mines have been found in Tekab and Qorweh in the East part of Kurdistan.
However, the most important sources that make people’s lives possible are drinkable water sources in the Middle East that emanate from the Kurdistan mountains and pour into Tigris and Euphrates rivers.