Part One
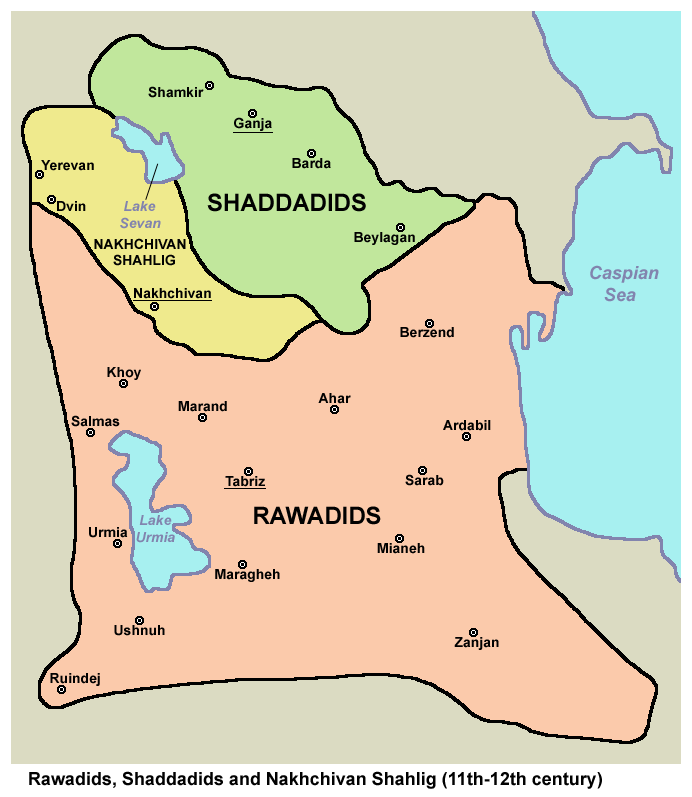
The Shaddadids were a Kurdish dynasty that ruled the Arran region and part of Armenia from the 4th to the 6th centuries AH (951 to 1199 AD). Arran is the name of a part of the Caucasus which its borders have changed throughout history. Geography scientists have called it Albania, Ariana, Rani, and Olvan, too.
The political geography of the Shaddadids’ rule included Ganja, Barda, Dabi, and Bilaqan, and sometimes their rule would extend to Georgia and part of the Byzantine Empire.
In addition to the main branch, the Shaddadids have another branch known as the Shaddadids of Ani because they settled in the city of Ani. It should be noted that Ani is a very old and well-known city in Armenia.
Munajjim-Bashi, the author of the book "Sahayef al-Akhbar fi Waghaye al-Athar", mentions a source called Tarikh al-Bab, which unfortunately no longer exists, and according to that source, he indicates that the Shaddadids were Kurds. In addition, "Ibn al-Athir" is another historian who considers the Shaddadids as a tribe of the Kurds of Rawadid and describes them as the most populous and largest Kurdish tribe. However, according to Ya'qubi, another famous historian, the Kurdish Rawadid, of whom the Shaddadids is a branch, differs from the Rawadids of Azerbaijan, who are of Arabic origin.
Before 340 AH, history records nothing about the Shaddadid family, but according to history, Mohammad Ibn Shaddad Ibn Qurtaq established their power in 340 AH after weakening the power of Ali Musafir, a Shiite family in northern Iran from present-day Gilan and controlled nearby Armenia.
Muhammad Ibn Shaddad chose the city of Dvin or Dabil, two Farsakh (about 10 km) far from the Aras River, as his capital, despite having political neighbors of famous powers such as Ali Buya (Buyid) and the Hamdanid. Muhammad was facing the attacks of Ibrahim Ibn Marzuban, the Emir of Ali Musafir, in the east, and Ashot III, the Emir of Georgia, in the west.
In a war between Ashot and Muhammad Shaddad, Ashot's army, consisting of Armenians, Georgians, and Lazgi, was much larger than Shaddad’s army, so Muhammad Shaddad ordered the people of Dvin to leave the city and ride their donkeys to frighten the Ashot army so that the enemy would be afraid to see more soldiers. Fortunately, the trick worked and they defeated the Ashot army.
Two years later, the Emir of Ali Musafir attacked the Shaddadids again. Some of Muhammad Shaddad's gate guards were on Ali Musafir's side and wanted to kill him. But Muhammad was not strong enough to fight back, thus he took refuge with his neighbor, and even asked the Byzantine Empire for help, it did not happen and he returned to Asforjan, where he had previously made a treaty of friendship with the Emir of Asfanjan and he died there. Although Muhammad ibn Shaddad had three sons, after their father's death they took refuge with Farisos, who ruled part of Arran, and later came into power again.
According to the Turkish-Iranian historian Ahmad Kasravi, Farisos gave the castle of Shamirom to the sons of Mohammad Shaddad, and in 370, they attacked the emir of Ganja from the castle and occupied the city.
However, according to the book of Munajjim-Bashi, Fadl Ibn Shaddad became a sheriff in the city of Ganja who gained people’s trust. Fadl was well known for being just and courageous; so, the people of Ganja entrusted Fadl with the city's responsibility and later offered the city's responsibility to Abul Hassan Lashkari,
Fadl's brother. However, the family of Ali Musafir again put pressure on the Shaddadids. This time, the conflict between the Shaddadids and Ali Musafir reached peace, and a peace treaty was signed between the two sides. Later, Abul Hassan established his power, expelled the Dailamites from Ganja, conquered much of the countries around Ganja, and died in 368 …
To be continued...